Manufacturing Process
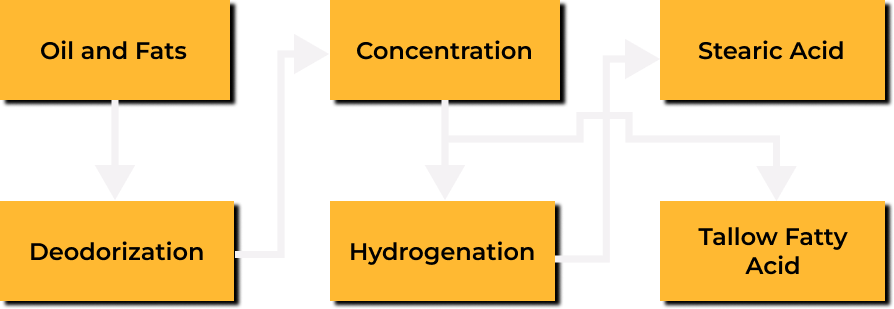
The production of stearic acid is initiated by the hydrolysis of fats and oils. Hydrolysis uses water to break the chains that bind chemical bonds. Triglycerides easily react with bases and acids and decompose at high temperature and high pressure (about 700 degrees Celsius, 5,000 kPa). This creates three fatty acid chains and one glycerin from one molecule of triglyceride. The mixture of fatty acids and glycerin is separated by washing. The solid fatty acid mixture remains while the liquid glycerin is washed away. The remaining fatty acid mixture is distilled to separate unwanted fatty acid chains and extract stearic acid.
Applications

1. Paint Industry
Stearic acid is a very effective wax modifier used in candle making. It is a non-toxic additive that increases the opacity and hardness of candles. It also increases candle whiteness and aids in holding the candle shape of freestanding candles in the warmer months. It increases the candle’s durability, consistency, and melting point. Due to its stability and shaping property it is used in making various art and craft products.

2. Detergent Industry
Stearic acid plays an important role in the manufacturing of soap and cosmetics such as face wash, shampoo, beauty soaps and shaving cream. Stearic acid acts as a thickener or hardener to help the soap to retain its shape. It is a powerful cleanser and also acts as an emulsifying agent to bind oil and water so it is used in facial cleanser, shampoos and shaving cream as it makes them soft and creamy.

3. Fragrance and Flavoring Industry
Stearic acid is a very effective wax modifier used in candle making. It is a non-toxic additive that increases the opacity and hardness of candles. It also increases candle whiteness and aids in holding the candle shape of freestanding candles in the warmer months. It increases the candle’s durability, consistency, and melting point. Due to its stability and shaping property it is used in making various art and craft products.
